Kidney Stones vs UTI: Exactly How to Recognize and Treat Each Condition Efficiently
Exploring the Effects and Causes of Kidney Stones in Comparison to Urinary System Tract Infections: A Thorough Guide
The expedition of kidney stones and urinary tract infections (UTIs) reveals a complicated interaction of signs and symptoms and underlying causes that warrant careful evaluation. What are the crucial distinctions in their signs and symptoms, and just how might these educate therapy strategies?
Summary of Kidney Stones
Kidney stones, also referred to as renal calculi, form when certain substances in the urine crystallize and aggregate, leading to the development of hard deposits within the kidneys. These rocks can differ in dimension, varying from a grain of sand to a golf sphere, and can be composed of different materials, the most usual being calcium oxalate, uric acid, struvite, and cystine. The development of kidney rocks is influenced by a number of elements, including nutritional behaviors, liquid consumption, and genetic predisposition.
Symptoms of kidney rocks might include severe discomfort in the back or side, blood in the pee, queasiness, and frequent urination, specifically as the rock moves through the urinary system system. Diagnosis generally involves imaging researches such as ultrasound or CT scans, along with urinalysis to determine the stone's make-up.
Treatment options differ based on the size and sort of stone, as well as the extent of signs (Kidney Stones vs UTI). Little rocks may pass naturally with raised fluid consumption, while larger stones might require clinical interventions such as lithotripsy or medical removal. Understanding the pathophysiology and threat elements connected with kidney rocks is important for reliable prevention and monitoring
Introduction of Urinary System Infections
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are common microbial infections that influence any part of the urinary system, consisting of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. They mostly occur when germs, commonly from the gastrointestinal tract, go into the urinary system, leading to inflammation and infection.
The frequency of UTIs is especially greater in women than males, mostly as a result of anatomical differences, such as a shorter urethra. Danger aspects consist of sex-related task, particular contraceptive approaches, urinary system retention, and dehydration. The medical diagnosis of UTIs is generally verified with urine tests, which may expose the existence of germs, white blood cells, or red blood cells.
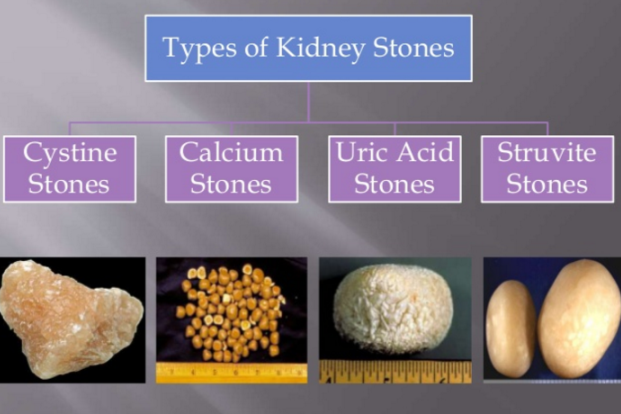
Signs of Kidney Stones
The discomfort associated with kidney rocks can show up in different methods, commonly leading people to seek medical focus. Among the most common signs and symptoms is extreme pain, generally localized in the reduced back or side, which might radiate to the abdomen or groin. This discomfort, commonly referred to as sharp or cramping, can occur suddenly and might change in intensity.
In addition, people may experience hematuria, or blood in the pee, which can vary from microscopic total up to visible staining. This sign may be come with by changes in urinary system practices, such as boosted frequency or seriousness, along with pain during peeing. Queasiness and throwing up are additionally widespread, frequently arising from the body's response to intense pain.
In many cases, individuals might useful source experience fever and cools, particularly if an additional infection develops because of the blockage brought on by the stones. On the whole, the combination of serious discomfort, hematuria, altered urinary patterns, and intestinal signs and symptoms can offer considerable understanding into the existence of web kidney rocks, warranting prompt medical analysis and treatment. Understanding these signs is vital for prompt diagnosis and effective administration of the condition.
Signs of Urinary System System Infections
Infections within the urinary system tract usually provide a series of unique signs and symptoms that can considerably affect day-to-day live. One of the most usual signs and symptoms consist of a persistent urge to urinate, frequently gone along with by a burning feeling during urination, referred to as dysuria. People might additionally experience raised regularity of peeing, generating little quantities of urine each time.
Other noteworthy symptoms include cloudy or foul-smelling urine, which might show the visibility of germs or pus. In some situations, urine may show up pink or red because of the existence of blood, a condition referred to as hematuria. In addition, people may experience pelvic discomfort or pressure, which can better aggravate the sensation of seriousness.
Systemic symptoms might likewise materialize, such as fever, cools, and tiredness, especially if the infection has actually ascended to the kidneys. It is necessary to recognize these signs and symptoms early, as unattended urinary tract infections can bring about a lot more severe difficulties. Kidney Stones vs UTI. Trigger medical focus is encouraged when these signs are observed, enabling ideal analysis evaluation and therapy to minimize pain and stop further wellness problems
Root Causes Of Each Condition
Regularly, kidney stones and urinary system tract infections occur from distinctive yet often overlapping reasons that can impact people in a different way. Kidney rocks usually create due to metabolic variables, dietary options, and hereditary tendencies. Increased levels of calcium, oxalate, or uric acid in the pee can result in rock development. Dehydration, insufficient liquid consumption, and high-sodium diets can worsen these conditions, promoting condensation within the urinary system tract.

Comprehending these distinct causes is essential for prevention and treatment. Kidney Stones vs UTI. While way of life adjustments may alleviate the threat of kidney rocks, suitable hygiene and timely treatment of urinary system tract infections are necessary for lowering their recurrence and associated problems
Verdict
In recap, kidney stones and urinary system system infections present distinctive signs and underlying reasons. Kidney rocks are identified by serious discomfort and metabolic elements, while urinary system tract infections mainly include bacterial infections bring about urinary necessity and pain. Both problems can result in hematuria, their development mechanisms differ dramatically. Understanding these differences is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment, ultimately improving person end results for those influenced by either condition.
The expedition of kidney stones and urinary tract infections (UTIs) discloses a complex interplay of signs and underlying reasons that require mindful examination.Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are typical bacterial infections that impact any component of the urinary system, consisting of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra.Frequently, kidney stones and urinary system tract infections find out occur from unique yet sometimes overlapping causes that can affect people in different ways.In recap, kidney stones and urinary system tract infections present distinct signs and underlying reasons. Kidney rocks are identified by extreme pain and metabolic factors, while urinary tract infections mostly entail microbial infections leading to urinary necessity and pain.